Vision-Robot Bridge (VRB) integrates vision with robotics by learning affordances—specifically contact points
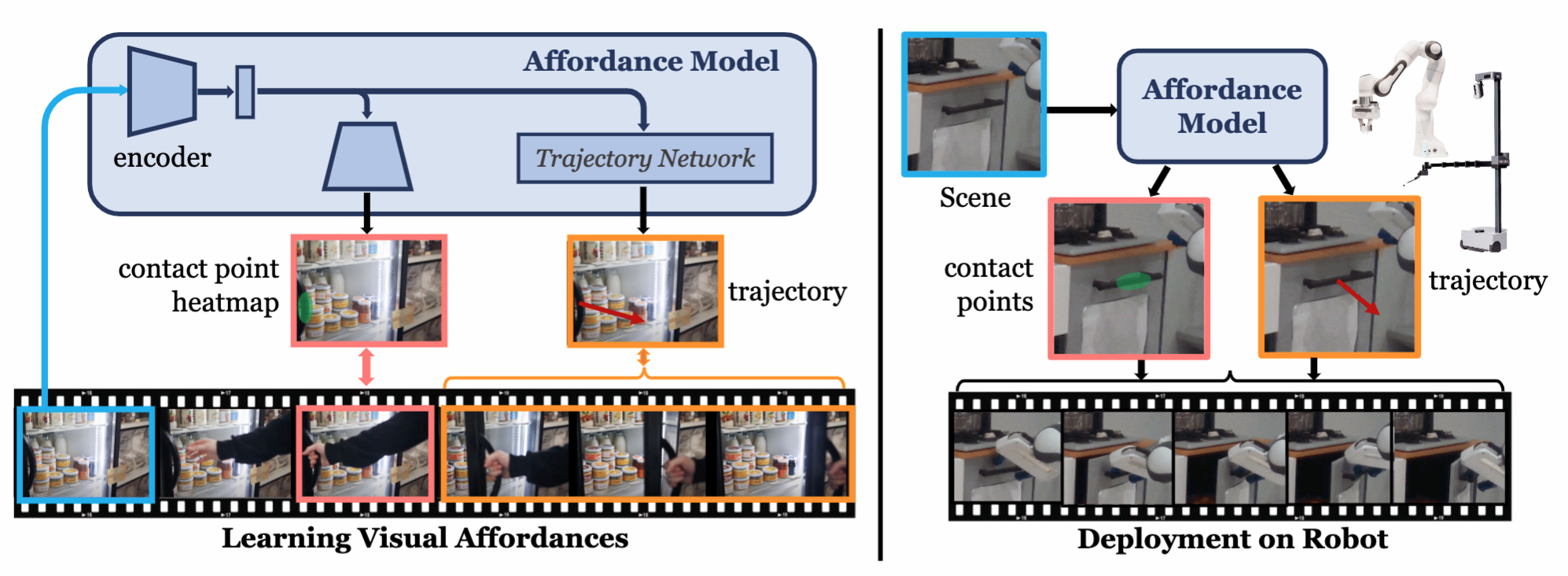
To extract this information from the video dataset, we perform the following steps:
- For each frame, use a hand-object detector to get bounding boxes and a discrete contact variable; find the first timestep where contact occurs.
- Compute a hand segmentation and compute all points where the hand intersects the object’s bounding box. Fit a GMM (
and ) on these contact points. - Note that due to camera motion, these points are projected back into the coordinate space of the initial frame by computing homographies.
- To avoid domain shift from human to robot hands, the contact points and post-contact trajectories are paired with the initial frames without human hands.
- Track the change of the hand’s bounding box as our post-contact trajectory.
- Train a predictive model to take in an image frame and output this GMM. This predictive model first runs the image through a backbone (ResNet), then uses
deconvolutional heads to model the multi-modal distribution of contact point heatmaps. The trajectory predictor, implemented as a Transformer, takes the backbone’s output and predicts relative shifts.
The trained model
- Imitation learning: rather than collecting human demonstrations, we can use
to guide the robot and create interesting trajectories. These can then be filtered and used with BC to train a policy. - Reward-free exploration: use
to bootstrap exploration; learn a distribution of the top trajectories, and then either sample from or use . - Goal-conditioned learning: fit
to top trajectories, then learn from them to minimize distance with goal image.