For random variable
In other words, applying the function to the expectation after gives us a smaller value than applying it first. If we apply this to two possible values
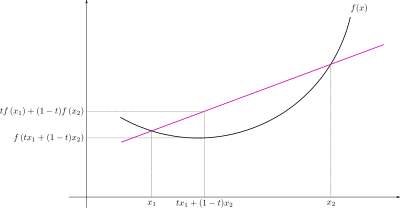
Jensen’s inequality works for concave functions too, with the inequality sign flipped:
This inequality is commonly used with the logarithm, giving us