Abstract
A transformer is a deep learning model that inputs and outputs sequences of tokens. It relies on the attention mechanism for transforming information, allowing it to make connections between different tokens within the same sequence as well as between the input and generated output.
Transformers are encoder-decoder models for sequence processing that only use the 🚨 Attention, leaving out the recurrence connections found in 💬 Recurrent Neural Networks. In other words, while RNNs process sequences word by word, transformers look at them in parallel.
We use the scaled dot-product attention, a slightly modified version of the general attention mechanism, which is calculated as
where
Info
This scaling factor of
is introduced to keep the variance at (instead of scaling with the dimension size), which prevents vanishing gradients in extreme areas of the softmax.
This mechanism is used in the multi-headed self-attention component, which applies it

In the following example, we can see that when analyzing “it,” one head focuses on “animal” and the other on “tired.”
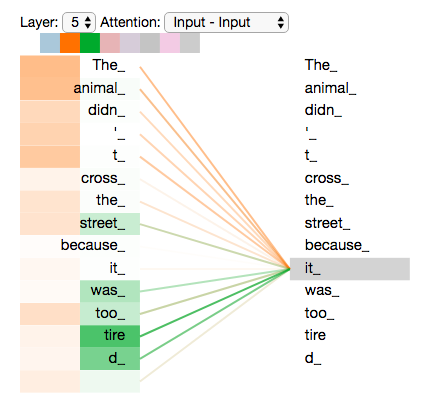
Transformers use multiple multi-head attention components in its encoders and decoders to extract sequence structure, which are then processed by feed-forward neural networks.
Architecture
The architecture is below. Our encoder takes in the entire sequence at once to calculate
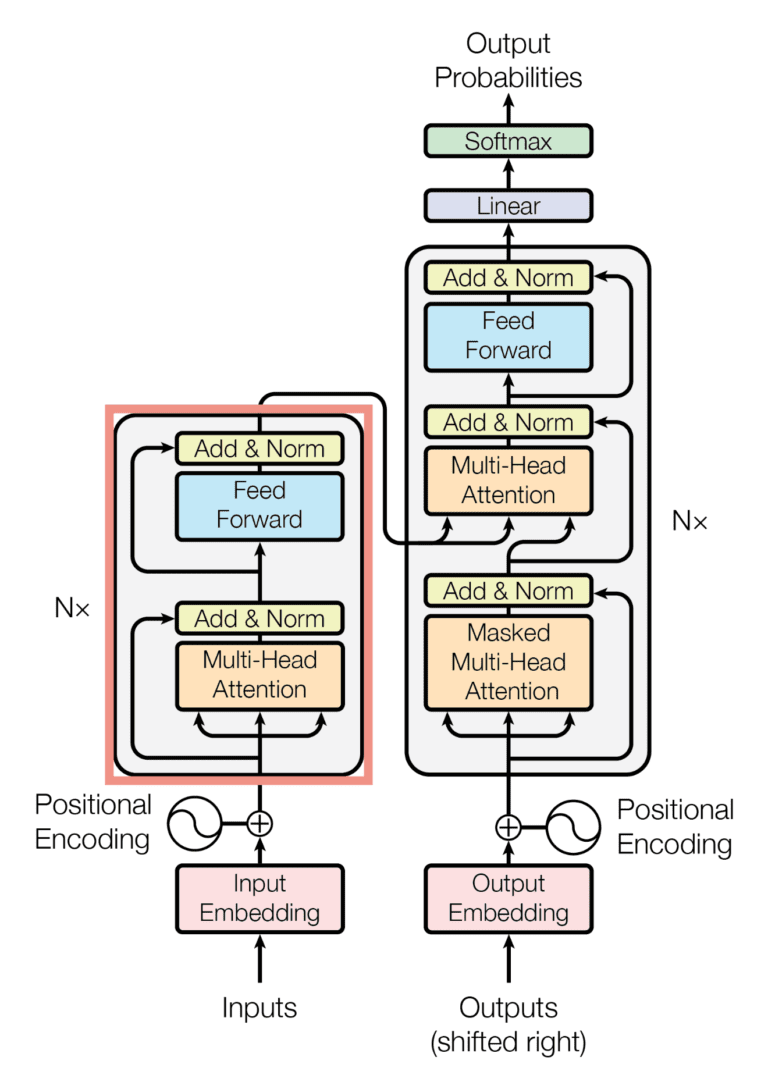
Each encoder unit uses a single self-attention mechanism, which uses the embedding or previous encoder unit output as queries, keys, and values.
Each decoder unit uses a masked self-attention mechanism (bottom) and a standard attention mechanism (top) that uses queries from the previous decoder output and keys and values from the encoder. We mask all rightward information in the former since the decoder should only use its previous output.
The feed-forward blocks are simple neural networks that calculate
Lastly, since we convert the each input token into an embedding, we maintain positional information for each token by adding a positional encoding, calculated with sines and cosines, that determine the distances between words.
Prediction
First, we run the entire input through the encoder to generate the keys and values used in the decoder.
To predict the next token, we give the decoder our previously generated sequence and receive softmax probabilities as output, which we use to get the token with highest probability.