An occupancy network is a 3D reconstruction technique that models the [[🐰 Shape Representations#Implicit Fields#Occupancy Field]] conditioned on a specific input object representation
which assigns occupancy probabilities for each point.
In implementation, we treat
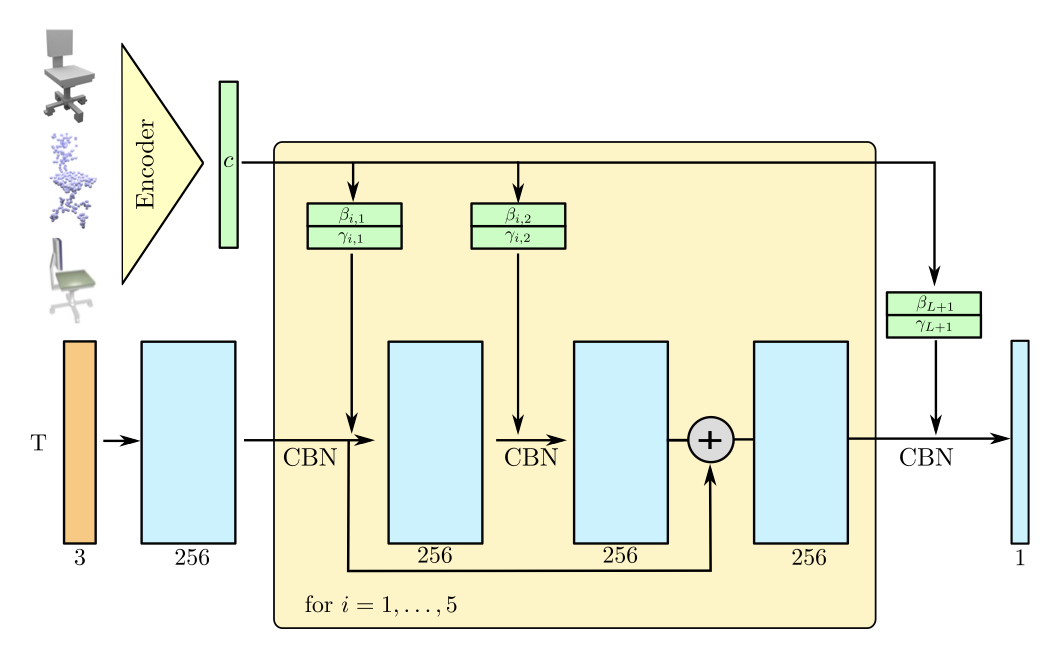
The encoder is task specific; we use ResNet for images, 🎾 PointNet for point clouds, and 3D CNN for voxels.

Optimization
To train our network, we randomly sample points
where
Inference (MISE)
To provide a 3D reconstruction using a trained occupancy network, we require a series of refinement steps; this algorithm is called multiresolution isosurface extraction (MISE).
- Discretize the volumetric space and evaluate
for all points on the grid; is some threshold, and all predictions above it indicate an occupied point. - Mark voxels as active if they have
adjacent grid points with different occupancies. This gives us the surface of the mesh. - Divide active voxels into eight subvoxels and repeat from step one until the desired resolution.
- Apply marching cubes to extract an isosurface.
- Simplify the mesh using Fast-Quadric-Mesh-Simplification.
- Refine the mesh using gradients from the occupancy network by minimizing
with respect to the mesh points
Convolutional Occupancy Network
Convolutional occupancy networks apply local information in occupancy prediction by using a more complex procedure than a simple FCN; rather than conditional on a global encoding of the input, we localize the features that are used in the occupancy network.

We first use a plane or volume encoder to process the input point cloud and collect them in a quantized grid. These grids are then processed by a U-Net, and local features from the grid are inputted to the occupancy prediction. These local features are defined as follows:
- For the single-plane encoding, use a bilinear sample from the projected position of the query point onto the grid.
- For the multi-plane encoding, project the plane onto all three dimensional planes and aggregate the features via summation.
- For the volume encoding, use trilinear interpolation for the voxel cell the query point lies in.